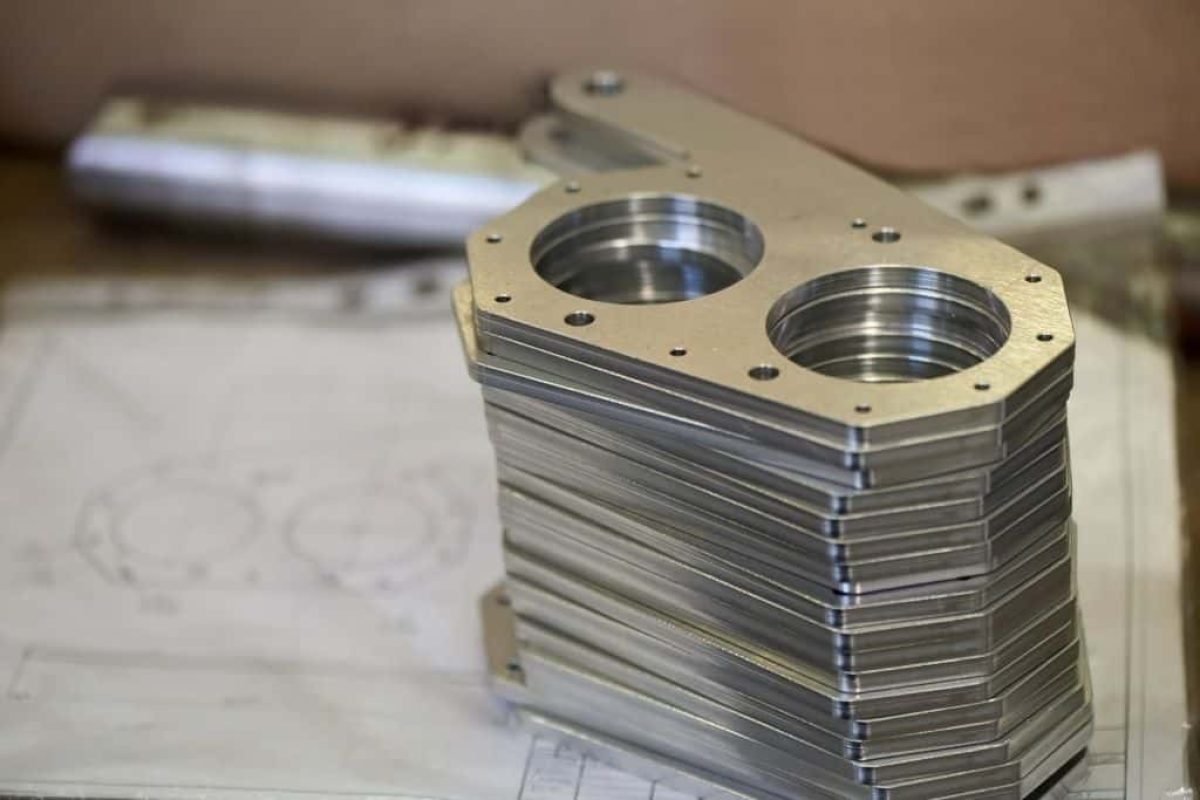
CNC milling and laser cutting are precision engineering techniques that are pivotal in manufacturing complex or high-tolerance components. Both methods have unique strengths and applications and are used extensively in industries ranging from medical and automotive to aerospace and woodworking.
While both CNC milling and laser cutting are integral to modern manufacturing, they employ distinctly different techniques in material handling.
What sets them apart, and how can you determine the most suitable method for your specific project needs? Let’s delve into the nuances of each technology.
What Is CNC Milling?
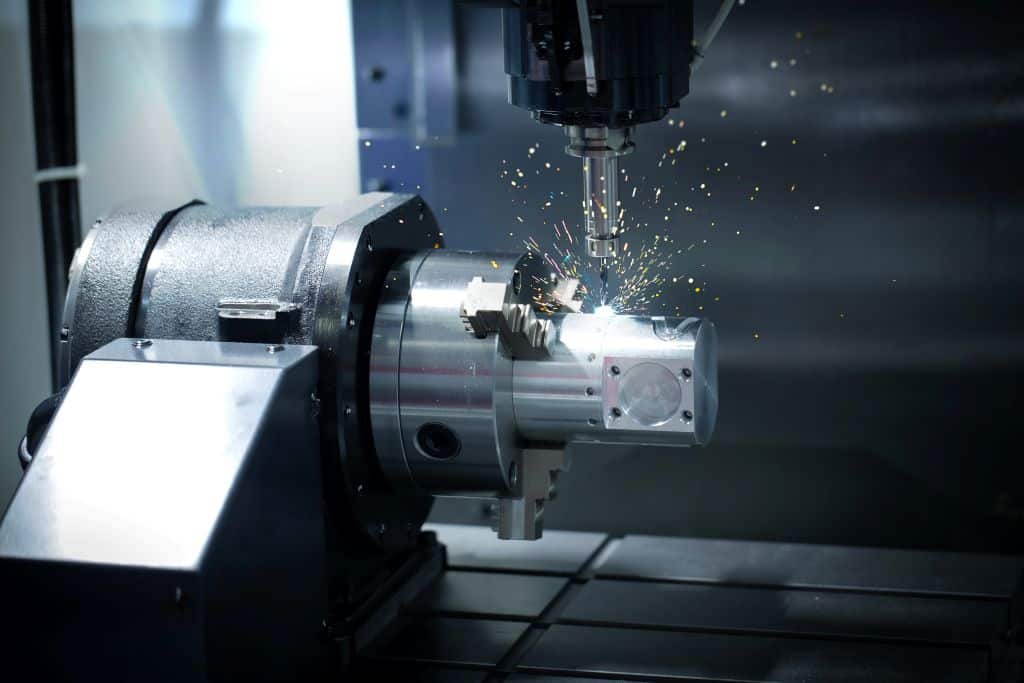
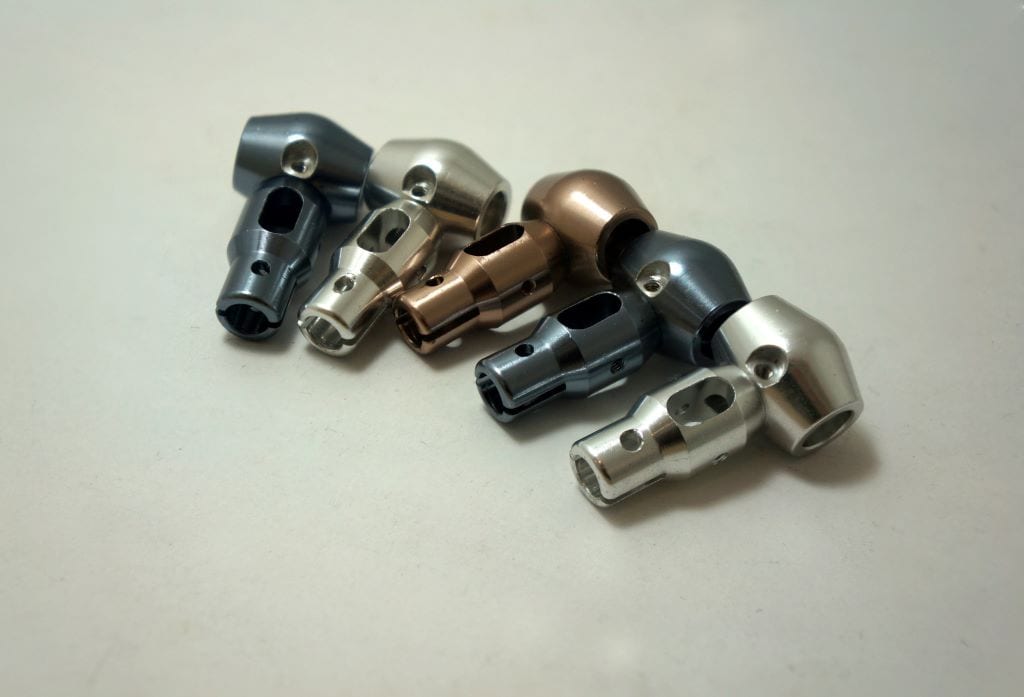
CNC milling is a cornerstone in precision machining. This technique uses computer numerical control (CNC) technology to manipulate rotary cutters and remove material from a workpiece. This process transforms a solid block of material into a final product by subtracting material. Materials commonly used in CNC milling include:
- Metal Billet: Ideal for creating sturdy, high-tolerance parts for industrial applications
- Wood: Perfect for detailed carvings and engravings in woodworking projects
- Plastics: Such as acrylic and nylon, which are suitable for creating precise components
- Composites: Like carbon fiber, which is favored for its strength-to-weight ratio in the aerospace and automotive sectors. It’s important to note that these materials require special CNC tooling.
- Foam: Used in prototyping and model making due to its ease of machining and low cost
The beauty of CNC milling lies in its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision. This precision would be impossible to replicate manually.
During CNC milling, the material is held firmly on a bed or holding device. Various cutting tools, including end mills and drill bits, rotate at high speeds to shape the piece.
The movements are pre-programmed in digital designs by skilled technicians. This method allows for intricate detailing and precise control over dimensions. The result is parts that fit perfectly into their intended uses with little to no finishing required.
How Much Does CNC Milling Cost?
Determining the cost of CNC milling projects involves several factors that significantly influence the final pricing:
- Material Type: Machining aluminum is generally less expensive than harder metals like titanium or stainless steel, which affect cutting speeds and tool wear.
- Design Complexity: More intricate designs require longer machining times and more advanced tool paths, increasing operational costs.
- Production Volume: Larger quantities typically reduce the cost per unit due to economies of scale.
- Finish Requirements: Additional costs may occur for finishes such as anodizing, powder-coating, or heat-treating.
Despite these variables, CNC milling remains highly valued for its precision and flexibility. It often proves to be a cost-effective solution for manufacturing custom components across various industries.
What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is an advanced manufacturing technique that employs a concentrated beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize material along a specified path guided by computer-controlled systems.
This process stands out for its accuracy and speed, making it ideal for detailed cuts on flat sheet materials.
Materials commonly used in laser cutting include:
- Metal Sheets: Such as stainless steel, aluminum, and brass, which are smoothly cut with high precision
- Acrylic: Known for its clean edges and smooth finishes when cut with a laser
- Wood: Including plywood and medium-density fiberboard, which are popular for fine art and decorative projects
- Fabric: Capable of being cut without fraying, ideal for textile design and production
- Paper and Cardboard: Perfect for intricate designs in paper crafts and packaging
The focused laser beam has such intense energy that it easily cuts through even hard materials with minimal kerf width (the width of material removed).
This technology excels in cutting and engraving surfaces without direct contact with the material, which avoids mechanical wear and tear on tools. It can also make extremely fine cuts for intricate patterns in metal arts or industrial components.
How Much Does Laser Cutting Cost?
The operational costs of laser cutting are influenced by several key factors that determine its overall affordability:
- Power Consumption: Costs are directly related to the wattage of the laser.
- Speed of Execution: Faster cuts can reduce operating times and costs.
- Gas Usage: Necessary for certain types of lasers, which impact overall expenses
- Material Type: Metals, plastics, and wood require different settings due to their unique properties.
Laser cutting offers a practical solution at competitive prices despite generally higher setup costs than other methods. Laser cutting excels at jobs with smaller volumes or highly detailed small parts that require precise cuts. Another advantage is a lower risk of damage or deformation from excess heat exposure (a risk in some traditional processes).
CNC vs. Laser
When deciding between CNC milling and laser cutting, consider the key differences that could influence your project’s requirements:
- Precision: Both techniques offer high precision, but laser cutting often edges out with its ability to produce extremely fine details.
- Material Thickness: CNC milling is more effective for thicker materials, while laser cutting is ideal for thinner sheets. CNC milling is often better for three-dimensional alterations as the material can be rotated and spun in the machine, while laser cutters often work better on two-dimensional paths.
- Material Type: While both methods can handle various materials, laser cutting struggles with reflective metals unless you’re using specialized lasers.
- Production Speed: Laser cutting is generally faster than CNC milling for simple cuts on thin materials.
- Setup Time: CNC milling requires more setup time than laser cutting.
- Cost Efficiency: Laser cutting can be more cost-effective for large volumes or detailed small parts due to lower labor costs and faster processing times.
- Material Preservation: Laser cutting generally removes less material than CNC milling making it more cost-effective for expensive base media.
In both cases—CNC milling and laser cutting—the choice boils down to your specific project requirements.
When to Use CNC Milling
CNC milling is advantageous in various manufacturing scenarios where precision and versatility are paramount. Consider employing CNC milling in the following situations:
- Complex Geometric Designs: Ideal for parts with intricate features or requiring multiple machining operations from various angles
- Heavy Duty Materials: Perfect for handling robust materials like steel, titanium, and other hard metals that require substantial material removal
- Prototyping: Excellent for creating detailed prototypes requiring exact testing and development specifications
- Custom Tooling: CNC is often used to create custom tools, molds, or components needed for specialized machinery or products.
These applications benefit significantly from CNC milling because they can precisely shape materials according to complex designs and high tolerance requirements.
When to Use Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is an excellent choice when speed and precision are needed without direct contact with the material. Here are some ideal scenarios for choosing laser cutting:
- Detailed Patterns and Fine Cutting: Best for materials requiring intricate cuts or delicate patterns, such as decorative panels or detailed mechanical components
- High-Speed Production: Suitable for projects demanding quick turnaround times on large batches of thin materials
- Materials Sensitive to Physical Contact: Optimal for materials that could be damaged or deformed by mechanical cutting methods
- Consistency Across Large Volumes: Useful when needing consistent results across high volumes without variation
Laser cutting is effective for projects that demand exactitude and fine detailing, especially when working with sheet metals, plastics, and other flat materials.
Laser Cutting and CNC Milling Made Easy
Choosing between CNC milling and laser cutting boils down to your project’s specific requirements regarding material type, thickness, detail needed, volume, and budget constraints.
At Armes Precision, we harness both technologies efficiently while ensuring top-notch quality, adhering to ISO 9001:2015 standards. Whether it’s detailed cuts via our state-of-the-art laser cutting services or robust shaping through CNC milling, our team is equipped to deliver perfection tailored to your needs.
Request a quote today for your laser cutting or CNC needs. Let us help you decide the best process tailored to your project requirements.